ESP32 CAN
The ESP32 has an integrated CAN controller and therefore doesn’t necessarily need an external controller. You only need to specify the RX and TX pins. Any GPIO will work.
# Example configuration entry
canbus:
- platform: esp32_can
tx_pin: GPIOXX
rx_pin: GPIOXX
can_id: 4
bit_rate: 50kbps
on_frame:
...Configuration variables
rx_pin (Required, Pin): Receive pin.
tx_pin (Required, Pin): Transmit pin.
rx_queue_len (Optional, int): Length of RX queue.
tx_queue_len (Optional, int): Length of TX queue, 0 to disable.
tx_enqueue_timeout (Optional, Time): Maximum time to wait when the TX queue is full before dropping the message (by default, this is set to the time it takes to send 10 CAN messages at the given bit rate).
All other options from Canbus.
The following table lists the bit rates supported by the component for ESP32 variants:
| bit_rate | ESP32 | ESP32-C3 | ESP32-C6 | ESP32-H2 | ESP32-S2 | ESP32-S3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 5KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 10KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 12K5BPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 16KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 20KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | |
| 25KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 31K25BPS | ||||||
| 33KBPS | ||||||
| 40KBPS | ||||||
| 50KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 80KBPS | ||||||
| 83K38BPS | ||||||
| 95KBPS | ||||||
| 100KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 125KBPS (Default) | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 250KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 500KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 800KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| 1000KBPS | x | x | x | x | x | x |
Wiring options
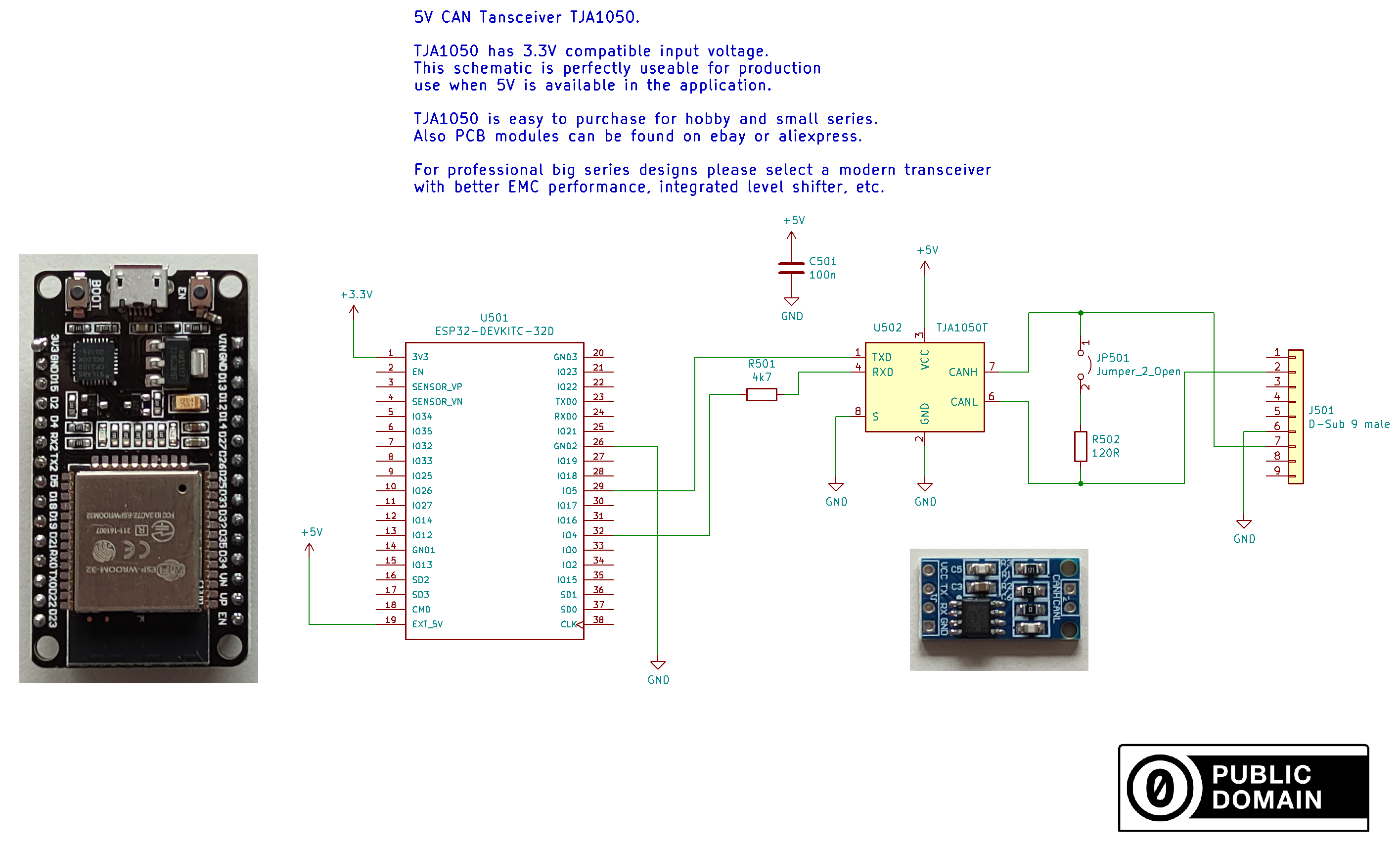
5V CAN transceivers are cheap and generate compliant levels. If you power your board with 5V this is the preferred option. R501 is important to reduce the 5V logic level down to 3.3V, to avoid damaging the ESP32. You can alternatively use a voltage divider here instead.
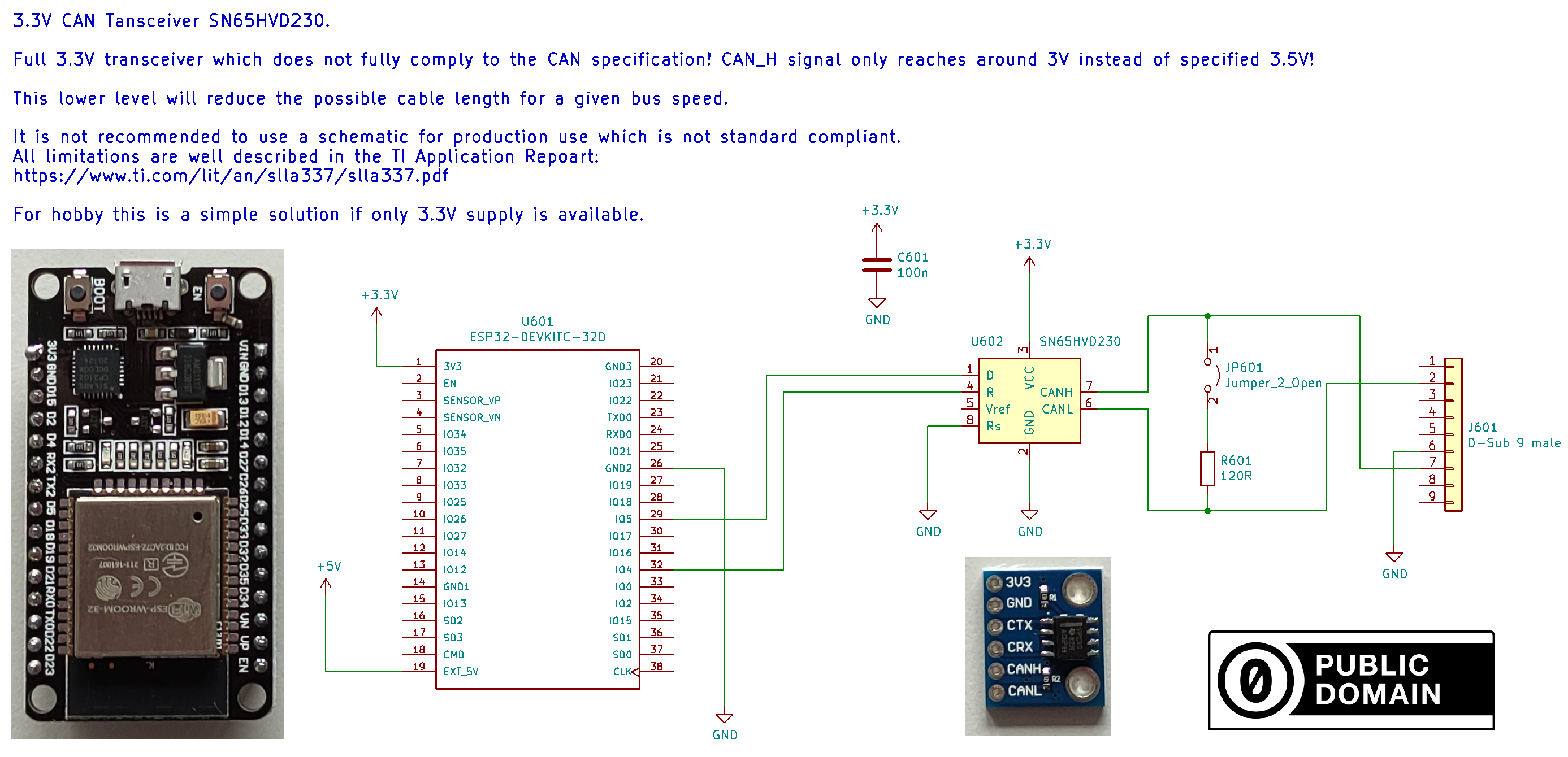
If you prefer to only have a 3.3V power supply, special 3.3V CAN transceivers are available.